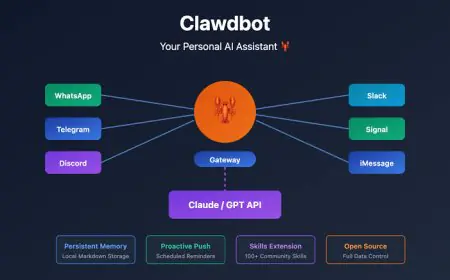
AI Bot Bandits: How OpenAI's Crawlers Are Bringing Down Small E-commerce Sites
The rise of OpenAI's crawler bots poses significant threats to small e-commerce sites, mirroring DDoS attacks and raising concerns over data security and intellectual property rights.

On January 10, 2025, a significant incident involving OpenAI's web crawler highlighted the potential risks of automated data scraping on online platforms. Triplegangers, a small e-commerce company specializing in 3D image files of human models, experienced a catastrophic disruption when OpenAI's bot attempted to scrape its entire website. The bot's relentless activity, described by Triplegangers' CEO Oleksandr Tomchuk as akin to a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, overwhelmed the company's servers, rendering the site inaccessible during critical business hours.
The issue stemmed from the absence of a properly configured `robots.txt` file on Triplegangers' website, which allowed OpenAI's crawler to interpret unrestricted access as permission to scrape. The bot reportedly made "tens of thousands" of server requests, utilizing over 600 IP addresses to download hundreds of thousands of photos and detailed product descriptions from the site. This activity not only disrupted the platform but also led to increased operational costs, including higher AWS bills, as reported by TechCrunch.
Triplegangers, a seven-person company, has spent over a decade building what it claims to be the largest database of "human digital doubles" on the web, catering to industries such as video game development and 3D artistry. The website's extensive database, comprising over 65,000 product pages, became the unintended target of OpenAI's bot, which was designed to gather data for training large language models like GPT-4 and GPT-5.