China's Humanoid Robots Harness AI to Revolutionize Production
China is moving to automate manufacturing, thanks to massive government funding and rapid AI advances.
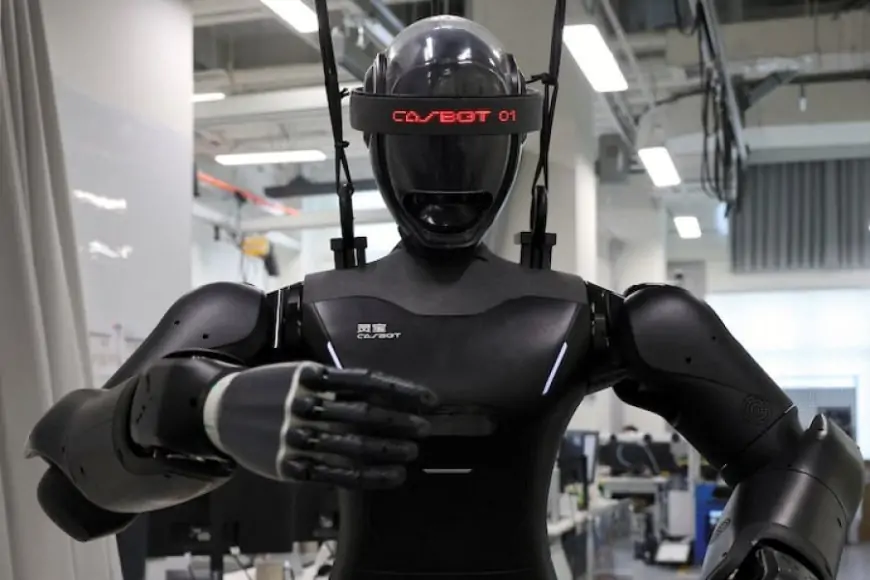

In a sprawling warehouse in a Shanghai suburb, dozens of humanoid robots are manoeuvred by their operators to carry out tasks like folding a T-shirt, making a sandwich and opening doors, over and over again.
Operating 17 hours a day, the site’s goal is to generate reams of data that its owner, Chinese humanoid startup AgiBot, uses to train robots it hopes will become ubiquitous and change the way humans live, work and play.
“Just imagine that one day in our own robot factory, our robots are assembling themselves,” said Yao Maoqing, a partner at AgiBot.
The importance of humanoid robots to Beijing, as it looks for solutions to pressing issues including trade frictions with the US, population decline, and slowing growth, was underscored when Chinese President Xi Jinping inspected AgiBot’s robots in Shanghai last month. Xi jokingly remarked during the visit that perhaps the machines could play in a football team.
Leading a Revolution
As the US negotiates with China over tariffs that President Donald Trump had imposed to help bring back US manufacturing jobs, Beijing is aiming for a new industrial revolution where many factory tasks would be performed by humanoid robots.
In recent years, Chinese humanoid robots have demonstrated increasing feats of agility, including performing somersaults, running a half-marathon, and even playing football, as Xi mused.
But Reuters is reporting for the first time details about how China’s advances in artificial intelligence, partly driven by the success of homegrown firms like DeepSeek as well as abundant government support, are allowing humanoid developers to pair the robots’ already impressive hardware with the software needed to make them economically valuable.
China aims to build its edge by focusing on data training and the sophistication of its AI models, the people said, with some saying the prowess of DeepSeek was a big aid.
A successful and widespread deployment of these robots in factory floors would enable China to keep driving economic growth and maintain its manufacturing superiority, making the field an area of competition with the US.
Government Backing
Chinese authorities are handing out generous subsidies for humanoid firms. More than $20 billion has been allocated to the sector over the past year, and Beijing is establishing a one trillion yuan ($137 billion) fund to support startups in areas such as AI and robotics, official announcements show.
The government is also a key buyer, according to a Reuters review of hundreds of tender documents. State procurement of humanoid robots and related tech jumped to 214 million yuan in 2024 from 4.7 million yuan in 2023. Other state support includes a newly created 10 billion yuan AI and robotics fund by the southern city of Shenzhen.
Humanoid robot makers and component suppliers based in Wuhan are eligible for subsidies of up to 5 million yuan after reaching thresholds for procurement and sales targets, as well as free office space.
Beijing’s municipal government created a robotics fund in 2023 that offered up to 30 million yuan for companies looking to accelerate construction of their first products. Some analysts predict that humanoids could follow the trajectory of electric vehicles, whose costs tumbled dramatically over the past decade as manufacturers rushed in and government subsidies spurred widespread adoption among the Chinese public.
The average bill of materials for a humanoid will be about $35,000 by the end of this year but could fall to $17,000 by 2030 if most of it is sourced from China, said Ming Hsun Lee, head of Greater China automotive and industrial research at Bank of America Securities, in a research note.
Three Chinese humanoid manufacturers told Reuters they predicted a similar halving of costs, perhaps within a year. In comparison, the component cost for Tesla’s (TSLA.O), Optimus robots, if all of their major parts are sourced from outside China, is currently $50,000 to $60,000, Lee added in the note. Tesla didn’t respond to a request for comment.
“With its comprehensive supply chain, China has an edge in lowering the humanoid robot production cost significantly,” Lee told Reuters, estimating that global humanoid robot annual sales could reach 1 million units in 2030. “This industry is still in its baby boom stage.”
Data Investments
The Chinese government is also investing heavily in data collection, which several executives said was the industry’s main pain point but also an area where China had an advantage.
In comparison to generative AI, where tech companies have trained foundation models by drawing from massive online datasets of text, pictures and audio, the supply of data necessary to train AI models used to run humanoid robots, also known as embodied AI platforms, is far smaller.
Humanoids need to interact with a physical environment and train on datasets focused on tasks, such as stacking boxes or pouring water into a cup.
Last year, Shanghai authorities assisted in setting up AgiBot’s data collection site, providing premises rent-free where about 100 robots operated by 200 humans work every day. AgiBot’s facility enables it to collect high-quality, targeted data, which it can use to train its embodied AI model, said Yao.
Similar sites are being built by governments in Beijing and Shenzhen, according to announcements. Widening deployment of humanoids, especially into factories, is likely to accelerate data collection.
China’s clearest advantage, however, is its domination of the hardware that makes up a humanoid. The country is capable of making up to 90% of humanoid components, lowering barriers to entry, according to analysts and startups.
As a result, China now accounts for the majority of manufacturers working on such projects globally and dominates the supply chain, according to Morgan Stanley. Some Chinese startups are selling robots as cheaply as 88,000 yuan ($12,178).
Jobs to be Affected?
While the industry remains incipient, Chinese lawmakers have begun to discuss the far-reaching implications intelligent humanoid robots could have for the workforce.
Some 123 million people work in manufacturing in China, according to a 2023 survey by the National Bureau of Statistics.
At this year’s National People’s Congress, social security expert Zheng Gongcheng warned that the development of robots and AI would affect around 70% of China’s manufacturing sector, which could lead to a steep decline in social security contributions.
At the same gathering, Liu Qingfeng, chairman of domestic AI firm iFlytek (002230.SZ) suggested the creation of an AI unemployment insurance program that would provide six to 12 months of coverage for workers replaced by robots.
Tang Jian, chief technology officer at the government-backed Beijing Innovation Centre of Human Robotics, told Reuters on the sidelines of the Beijing robot half-marathon in April that its prototypes were targeting jobs that humans don’t want to do due to their boring or repetitive nature, as well as dangerous tasks.
Despite concerns about the impact on jobs, Beijing sees the technology as key to plug labour shortages in areas such as elderly care, where demand is increasing as China’s 1.4 billion population ages.
China’s government published a national elderly-care plan in December that encouraged integration of humanoid robots and AI. Soon after, tech giant Ant Group announced the creation of a new subsidiary Ant Lingbo Technology, whose humanoid robots will focus on elderly care, among other areas.
“The robots in five or 10 years could organise a resident’s room, pick up a package or even transfer people from a bed to a washroom,” said AgiBot’s Yao.