Cochlear Achieves Edge AI Breakthrough with Machine Learning Implants Inside Human Body
Cochlear launches the Nucleus Nexa System, the world's first smart cochlear implant running machine learning algorithms inside the body for real-time environmental adaptation and personalized hearing solutions.
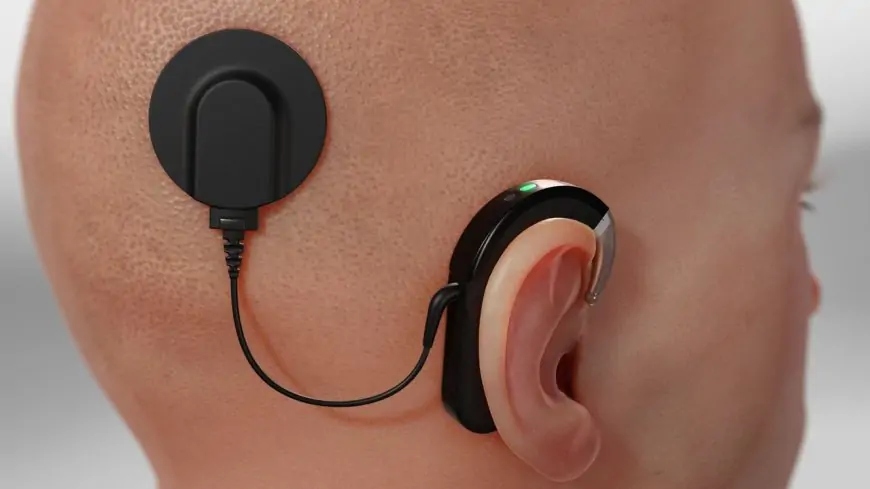
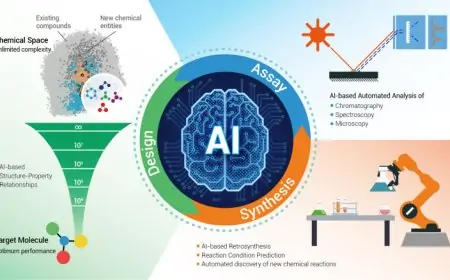
Cochlear has achieved a pioneering milestone in edge AI by deploying machine learning algorithms directly within cochlear implants implanted in the human body. The newly launched Nucleus Nexa System represents the first such device capable of running decision-tree models for real-time auditory environment classification, optimizing sound processing settings autonomously while managing extreme power constraints for decades-long operation.
At its core lies SCAN 2, an environmental classifier that analyzes incoming audio to categorize it as Speech, Speech in Noise, Noise, Music, or Quiet. This feeds into a decision tree machine learning model that dynamically adjusts electrical signals sent to the implant, enhancing speech clarity in complex real-world scenarios. The system also incorporates ForwardFocus spatial noise reduction, using dual microphones to filter background interference algorithmically without user input.
A groundbreaking feature is the implant's upgradeable firmware, delivered over-the-air via a secure short-range RF link from the external processor. This allows audiologists to update AI models and personalized hearing maps stored on-device, ensuring patients benefit from ongoing improvements without surgical intervention. The implant retains up to four user maps internally, enabling seamless processor replacement.
Power efficiency is achieved through Dynamic Power Management, where ML classifications guide energy allocation between the external processor and implant. This edge AI approach addresses ultra-low power demands—running continuous audio processing on batteries lasting full days—while maintaining imperceptible latency critical for natural hearing perception.
Cochlear's CTO Jan Janssen highlighted future expansions toward deep neural networks for superior noise handling and fully implantable systems with integrated microphones. This deployment sets a blueprint for edge AI medical devices, balancing interpretability, safety, and 40-year lifecycles in life-critical neural interfaces