Small Efficient AI Models Gain Ground for Everyday Devices and Remote Research
IBM Research and NASA introduce compact Earth-observation AI models designed for remote scientific use, highlighting a shift toward efficient AI capable of running on everyday devices and complementing large-scale systems.
Small, efficient AI models are rapidly gaining traction as their capabilities extend to operate effectively on everyday devices, ranging from smartphones to satellites. This trend offers a fresh perspective on AI development—focusing not only on raw power but also on accessibility, efficiency, and versatility.
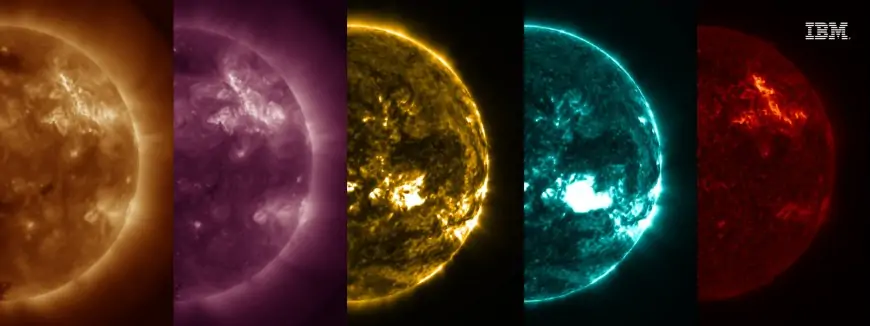
In a notable advancement, IBM Research and NASA jointly released smaller Earth-observation AI models tailored for challenging remote scientific research environments. These streamlined models are optimized to run on limited-compute platforms, making it possible to analyze environmental data directly on satellites or field instruments without relying on constant connectivity or large-scale cloud resources.
Unlike traditional large AI systems that demand significant processing power and infrastructure, these leaner models deliver high performance in specific tasks such as land cover classification, climate monitoring, and ecosystem assessment while maintaining low energy consumption. This enables expanded deployment in areas with constrained resources or intermittent connectivity.
The development signifies a complementary approach to AI innovation, where compact models coexist with massive AI architectures to form a diversified ecosystem. Large-scale systems continue to provide deep learning capabilities for complex problem-solving and massive datasets. At the same time, efficient smaller models promote democratization of AI by embedding intelligence into devices people use daily and instruments operating in remote locations.
IBM and NASA’s collaboration exemplifies the practical impact of this shift, pushing AI beyond centralized data centers to the edge of space and Earth’s most inaccessible regions. This accessibility accelerates real-time scientific insights and decision-making processes without compromising accuracy or reliability.
As AI adoption spreads across industries and geographies, the growing emphasis on smaller, efficient models reflects an industry trend prioritizing sustainability, cost savings, and user empowerment. This balanced AI future embraces diversity in model size, deployment scenarios, and functional roles, encouraging innovative applications even where traditional infrastructure is unavailable.
The success of these models encourages further research and development focused on model compression, energy efficiency, and adaptive algorithms—paving the way for broader AI integration in fields like agriculture, disaster response, environmental conservation, and space exploration.
By complementing the power of large AI frameworks with nimble, resource-conscious alternatives, the AI landscape is expanding toward inclusive, practical intelligence that meets the demands of an ever-more connected and environmentally aware world.